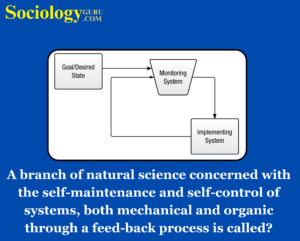
Question: A branch of natural science concerned with the self-maintenance and self-control of systems, both mechanical and organic through a feed-back process is called?
- Homeostatis
- Cybernetics
- Semantics
- None
Answer: (2)Cybernetics: Navigating the Self-Maintenance and Self-Control of SystemsCybernetics, a term derived from the ancient Greek meaning “helmsperson,” stands as a pivotal branch of natural science. It is dedicated to unraveling the intricacies of circular causal processes, particularly those involving feedback. At its core, cybernetics explores the self-maintenance and self-control mechanisms inherent in both mechanical and organic systems. This field, marked by its trans disciplinary nature, extends its reach across ecological, technological, biological, cognitive, and social domains, permeating practical activities like designing, learning, and managing. The Helmsperson’s Guidance:The metaphorical helm of a ship, manipulated by a helmsperson, serves as the quintessential example of circular causal feedback—the very essence of cybernetics. In the act of steering a ship, the helmsperson continuously adjusts their steering based on the observed effects, creating a feedback loop. This loop enables the maintenance of a steady course despite the ever-changing environment, responding adeptly to disturbances from crosswinds and tide. Cybernetics, in its origin, draws inspiration from this dynamic and adaptive process, emphasizing the significance of feedback in achieving stability and control. Circular Causal Processes Across Disciplines:The purview of cybernetics extends far beyond the maritime realm, encompassing a diverse array of disciplines. Whether in ecological systems, technological advancements, biological organisms, cognitive processes, or societal structures, circular causal processes are ubiquitous. Cybernetics, with its trans disciplinary character, serves as a unifying framework to comprehend and navigate these circular processes. From the regulation of ecosystems to the intricacies of human thought, cybernetics offers insights into how systems maintain equilibrium through feedback. Trans disciplinary Intersections:Cybernetics is not confined to the theoretical realm; it intersects with numerous fields, each contributing to its diverse interpretations and applications. The ecological dimension of cybernetics explores how natural systems self-regulate to adapt to environmental changes. In the technological sphere, cybernetics plays a crucial role in the design of self-regulating mechanisms, allowing machines to respond autonomously to varying conditions. The biological facet investigates the feedback loops within living organisms, illuminating the intricate processes of self-maintenance and adaptation. Cognitive Insights:Within the cognitive domain, cybernetics unveils the circular causal processes that govern learning, perception, and decision-making. Human cognition, akin to the helmsperson’s adjustments, operates through continuous feedback loops. Understanding these cognitive feedback mechanisms enhances our grasp of how individuals adapt to new information, learn from experiences, and make decisions in dynamic environments. Societal Systems and Practical Applications:In the realm of societal systems, cybernetics delves into the complexities of social structures and interactions. The principles of feedback guide analyses of organizational dynamics, management practices, and the design of structures that maintain equilibrium amidst internal and external stimuli. Cybernetics is not merely a theoretical construct; its practical applications in designing adaptive systems, facilitating learning, and optimizing management processes underscore its significance in navigating the complexities of our world. Challenges and Ethical Considerations:While cybernetics offers profound insights, it is not without challenges. The intricate nature of circular causal processes demands sophisticated modeling techniques and analytical tools. Ethical considerations come to the forefront, especially when dealing with cognitive and societal systems. Manipulating feedback loops raises questions about unintended consequences and the ethical implications of altering the self-maintenance mechanisms inherent in various contexts. Conclusion:In conclusion, cybernetics stands as a beacon in the exploration of circular causal processes, providing a holistic understanding of self-maintenance and self-control in diverse systems. From the helmsperson’s guidance in steering a ship to the ecological balance of natural ecosystems, from technological advancements to the intricacies of human cognition, cybernetics weaves a narrative of feedback-driven equilibrium. Its transdisciplinary intersections showcase the versatility of cybernetics, making it an indispensable framework across disciplines. The practical applications of cybernetics in designing adaptive systems, facilitating learning, and optimizing societal structures underscore its relevance in addressing real-world challenges. As technology advances and our understanding of complex systems deepens, the influence of cybernetics is poised to grow, guiding us through the dynamic and ever-changing landscapes of our interconnected world. |
Take a Quick Sociology Quiz to measure your Performance
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Question: Define the term “ethnic movement” and provide an example from India.
Answer: An ethnic movement refers to a collective effort by a group sharing common cultural, linguistic, or religious traits, seeking to assert their identity and rights; an example from India is the Khalistan Movement in Punjab.
2. Question: Identify the main objectives behind the Gorkhaland ethnic movement.
Answer: The Gorkhaland ethnic movement primarily seeks to establish a separate state for India’s Nepali-speaking population in the Darjeeling region, advocating for linguistic and cultural recognition and political autonomy.
3. Question: What was the Operation Blue Star, and which ethnic movement was it related to?
Answer: Operation Blue Star was a military action in 1984, aiming to remove Sikh militants hiding in the Golden Temple in Amritsar; it is related to the Khalistan movement, which sought a separate Sikh country.
4. Question: Mention a critical factor that triggered the emergence of ethnic movements in India, as discussed by Dipankar Gupta.
Answer: Dipankar Gupta emphasized that ethnicity is fundamentally a political process, wherein caste and religion, the key components of identity formation, are politicized by leaders for vested interests.
5. Question: What were the primary reasons for the Assam Ethnicity conflicts involving Bodo tribals and Bengali Muslim settlers?
Answer: The Assam Ethnicity conflicts primarily stemmed from issues related to immigration, land rights, and resource allocation, leading to clashes, riots, and evolving relationships among indigenous communities to address challenges.
6. Question: Briefly describe the role of the Dravidian Movement in terms of caste and societal structure.
Answer: The Dravidian Movement, led notably by E.V. Ramasamy, aimed to establish an egalitarian society, focusing on anti-Brahmanism and advocating for equal rights for backward castes, while also introducing reforms like self-respect marriages.
7. Question: Name the prominent ethnic movements in North-East India and specify one common objective.
Answer: Prominent ethnic movements in North-East India include the Nagas’ and Mizos’ struggles; a common objective was to gain autonomy and recognition for their distinct tribal identities and cultural uniqueness.
8. Question: What is the key argument of Gail Omveldt regarding traditional Indian society and multiculturalism?
Answer: Gail Omveldt opposed romanticizing traditional Indian society, arguing that hierarchy has always dominated it and dismissing the notion that multiculturalism is an intrinsic feature of Indian society as a myth.
9. Question: Briefly explain the social hierarchy factor as a contributing element to ethnic movements as suggested by Olzak.
Answer: Olzak suggests that the construction of hierarchies among ethnic communities, which often leads to the suppression of one group by another, is a key factor that can instigate social and ethnic movements.
10. Question: Identify one consequence of the unequal economic development factor within the context of ethnic movements in India.
Answer: One consequence of unequal economic development is the marginalization and underdevelopment of certain groups, leading to feelings of alienation and sometimes initiating ethnic movements as these groups strive for equality and recognition.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
META TAGS:
Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at SOCIOLOGY GURU guides students according to the Recent Trends, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology.
At Sociology Guru, the Best Sociology Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose The Best Sociology Teacher for your Preparation?
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Teacher, Best Sociology Coaching, Sociology Syllabus.
Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology, Sociology Coaching, Best Sociology Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology CUET, Sociology for IAS, Sociology for UPSC, Sociology for BPSC, Sociology for UGC NET, Sociology for JPSC,
Follow us :
KEYWORD: -Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, Mechanical and Organic, MA CUET SOCIOLOGY